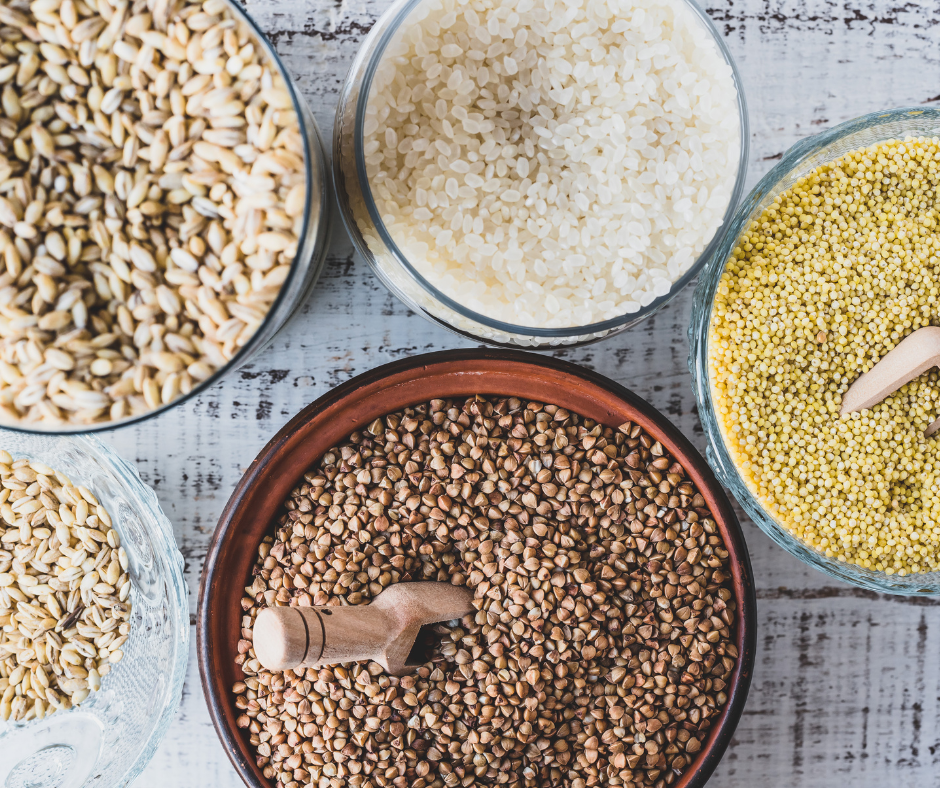
Millet is a group of grasses with small seeds that have been grown and eaten for thousands of years. Millet has been gaining popularity recently due to its nutritional value, gluten-free nature, and ability to grow in harsh environmental conditions.
Millets is an environmentally friendly crop that requires fewer resources than other major cereal crops like wheat and rice. It is a hardy crop that can withstand drought, heat, and pests, making it a reliable food source even in unfavorable climatic conditions. Additionally, millets is a versatile crop that can be grown in different types of soils, including marginal lands unsuitable for other crops.
Millets cultivation promotes sustainable agriculture practices, such as crop rotation and intercropping, which improve soil fertility, reduce soil erosion, and promote biodiversity. This, in turn, leads to healthier ecosystems and more resilient communities. Furthermore, millets is a cost-effective crop that benefits farmers economically, particularly in areas where it is the main crop grown.
In this article, we will explore how millet is an environmentally, ecologically, and economically friendly source of food and nutrition. We will look at how good it is for you, how it affects the environment, and how growing it helps with sustainable farming.
Nutrional value of millets:
Millets is a highly nutritious grain that is rich in essential nutrients. Here are some of the key nutritional benefits of millets:
1. Carbohydrates:
Millets is an excellent carbohydrate source that provides the body with energy. It has a low glycemic index, meaning it does not cause a rapid increase in blood sugar levels.
2. Protein:
Millets is a good source of plant-based protein, containing about 10–15 percent protein by weight. This makes it an excellent protein source for vegetarians..
3. Fiber:
Millet has a lot of fiber, which helps keep your digestive system healthy and keeps you from getting constipated. It also helps to reduce cholesterol levels and lower the risk of heart disease.
4. Vitamins and Minerals:
Millet is rich in vitamins and minerals, including B vitamins (thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, and B6), folate, calcium, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, and potassium.
5. Antioxidants:
Millet is a good source of antioxidants, which help to protect the body from oxidative stress and prevent chronic diseases such as cancer and heart disease.
Impacts of Millet on the Environment:
Millet cultivation has several positive impacts on the environment. Here are some ways millets is environmentally friendly:
1. Drought Tolerance:
Millet is a drought-tolerant crop that can grow in areas with low rainfall. This means it requires less water than other cereal crops like wheat and rice, making it a more sustainable option in areas with water scarcity.
2. Soil Conservation:
Millet is an excellent crop for soil conservation. Its deep root system helps to prevent soil erosion, while its ability to fix nitrogen in the soil improves soil fertility.
3. Biodiversity:
Millet cultivation promotes biodiversity by providing habitats for insects, birds, and other wildlife. Additionally, millets can be grown in mixed cropping systems, and planted with other crops like legumes or vegetables, further enhancing biodiversity.
4. Low Chemical Input:
Millet is a low-input crop that requires fewer fertilisers and pesticides than other cereal crops. This reduces the environmental impact of farming and promotes sustainable agriculture practices.
5. Climate Resilience:
Millet is a climate-resilient crop that can adapt to changing environmental conditions such as drought and heat. This makes it a more reliable crop in areas where climate change is expected to impact agriculture significantly.
How Millets Cultivation Supports Sustainable Agriculture Practices?
Millet cultivation promotes sustainable agriculture practices in several ways. Here are some of the ways how millets supports sustainable agriculture:
1. Crop Rotation:
Millet can be grown as part of a crop rotation system, which helps to improve soil health and reduce the risk of soil-borne diseases. Crop rotation also reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, promoting more sustainable farming practices.
2. Intercropping:
Millets can be intercropped with legumes or other crops, which helps to improve soil fertility and increase crop yields. Intercropping also promotes biodiversity and reduces the risk of crop failure.
3. Water Conservation:
Millet is a drought-tolerant crop that requires less water than other cereal crops like wheat and rice. This makes it a more sustainable option in areas with water scarcity.
4. Low Chemical Input:
Millet is a low-input crop that requires fewer fertilizers and pesticides than other cereal crops. This reduces the environmental impact of farming and promotes sustainable agriculture practices.
5. Food Security:
Millet is a staple food for many people in developing countries, particularly in Africa and Asia. Its ability to grow in harsh environmental conditions makes it a reliable food source, contributing to food security and promoting sustainable livelihoods.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, millets is an environmentally, ecologically, and economically friendly food and nutrition source promoting sustainable agriculture practices. Millet cultivation has several positive impacts on the environment, including soil conservation, promoting biodiversity, reducing the environmental impact of farming, and improving water conservation. Millet is also highly nutritious, providing essential nutrients like carbohydrates, protein, fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
Additionally, millet’s ability to grow in harsh environmental conditions makes it a reliable food source, contributing to food security and promoting sustainable livelihoods. By helping people grow millets, we can help build food systems that are more sustainable and resilient, with a focus on environmental and social sustainability. Climate change and food insecurity are becoming major problems worldwide. Promoting the growing and eating of millets can help solve these problems and provide a healthy, long-lasting food source.
FAQs
1. How can millet farming promote soil conservation?
Millet’s deep root system helps to prevent soil erosion, while its ability to fix nitrogen in the soil improves soil fertility. Additionally, millet can be grown as part of a crop rotation system, improving soil health.
2. Is millet cultivation environmentally friendly?
Yes, millet cultivation is environmentally friendly. It is a low-input crop that requires less water, fertilizer, and pesticides than other cereal crops, reducing the environmental impact of farming. Millet also promotes biodiversity, conserves water, and is a climate-resilient crop.
3. Can millet cultivation help address food insecurity?
Yes, millet cultivation can help address food insecurity. Millet is a very healthy crop because it has important nutrients like carbs, protein, fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Its ability to grow in harsh environmental conditions makes it a reliable food source, contributing to food security and promoting sustainable livelihoods.